My current home stereo is a patchwork of various pieces I got on +flee markeds over the years. It is amazing what kind of equipment +show up there. I've been wondering for a while if it was possible to +measure how well this equipment is working together, and decided to +see how far I could get using free software. After trawling the web I +came across an article from DIY Audio and Video on +Speaker +Testing and Analysis describing how to test speakers, and it listing +several software options, among them +AUDio MEasurement +System (AUDMES). It is the only free software system I could find +focusing on measuring speakers and audio frequency response. In the +process I also found an interesting article from NOVO on +Understanding +Speaker Specifications and Frequency Response and an article from +ecoustics on +Understanding +Speaker Frequency Response, with a lot of information on what to +look for and how to interpret the graphs. Armed with this knowledge, +I set out to measure the state of my speakers.
+ +The first hurdle was that AUDMES hadn't seen a commit for 10 years +and did not build with current compilers and libraries. I got in +touch with its author, who no longer was spending time on the program +but gave me write access to the subversion repository on Sourceforge. +The end result is that now the code build on Linux and is capable of +saving and loading the collected frequency response data in CSV +format. The application is quite nice and flexible, and I was able to +select the input and output audio interfaces independently. This made +it possible to use a USB mixer as the input source, while sending +output via my laptop headphone connection. I lacked the hardware and +cabling to figure out a different way to get independent cabling to +speakers and microphone.
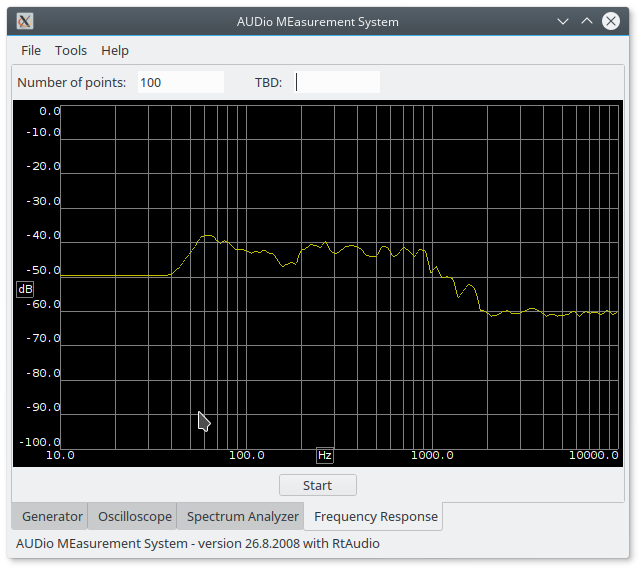
+ +Using this setup I could see how a large range of high frequencies +apparently were not making it out of my speakers. The picture show +the frequency response measurement of one of the speakers. Note the +frequency lines seem to be slightly misaligned, compared to the CSV +output from the program. I can not hear several of these are high +frequencies, according to measurement from +Free Hearing Test +Software, an freeware system to measure your hearing (still +looking for a free software alternative), so I do not know if they are +coming out out the speakers. I thus do not quite know how to figure +out if the missing frequencies is a problem with the microphone, the +amplifier or the speakers, but I managed to rule out the audio card in my +PC by measuring my Bose noise canceling headset using its own +microphone. This setup was able to see the high frequency tones, so +the problem with my stereo had to be in the amplifier or speakers.
+ +Anyway, to try to role out one factor I ended up picking up a new +set of speakers at a flee marked, and these work a lot better than the +old speakers, so I guess the microphone and amplifier is OK. If you +need to measure your own speakers, check out AUDMES. If more people +get involved, perhaps the project could become good enough to +include in Debian? And if +you know of some other free software to measure speakers and amplifier +performance, please let me know. I am aware of the freeware option +REW, but I want something +that can be developed also when the vendor looses interest.
+ +As usual, if you use Bitcoin and want to show your support of my +activities, please send Bitcoin donations to my address +15oWEoG9dUPovwmUL9KWAnYRtNJEkP1u1b.
+ +